Regenerative Farming is a way of growing food that works with nature, not against it. It is based on the idea that healthy soil is the foundation of healthy food, healthy people, and a healthy planet.
It aims to restore the natural balance of the soil, increase its fertility, and enhance its ability to store water and carbon.
By doing so, it can help combat climate change, improve food security, and support biodiversity.

What Is Regenerative Farming?
Regenerative farming is not a new concept, but rather a rediscovery of ancient wisdom and practices that have been used by indigenous and traditional farmers for centuries.
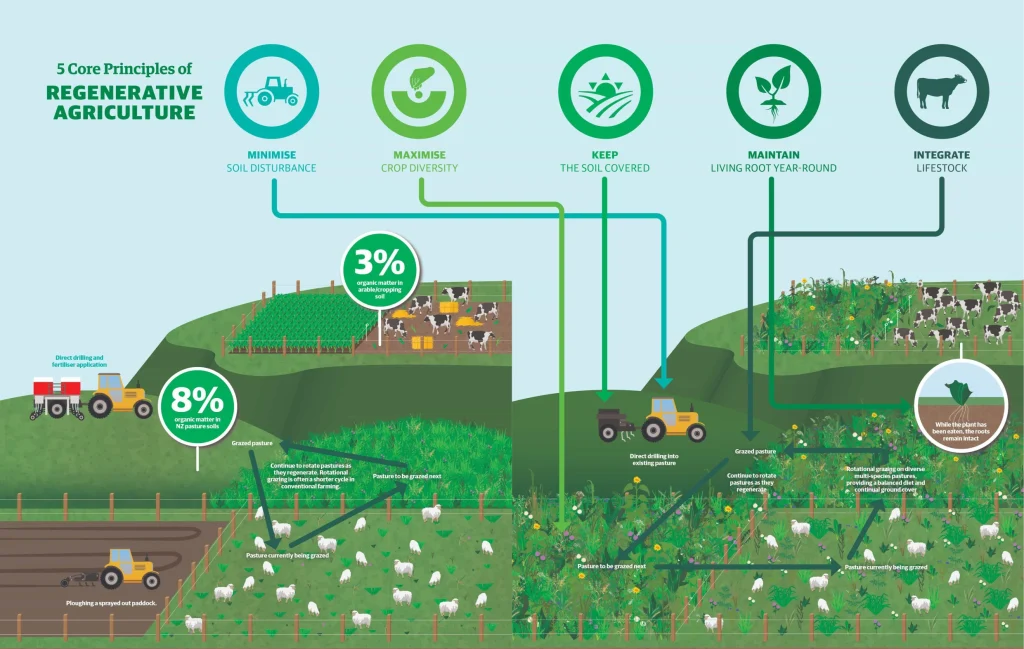
This is also not a one-size-fits-all approach, but rather a set of principles and practices that can be adapted to different contexts and climates. Some of the common elements of regenerative farming are:
No-till Or Low-till Farming
This means avoiding plowing or disturbing the soil as much as possible, which can damage its structure and release carbon into the atmosphere.
Regenerative farmers use cover crops, mulches, and composts to nurture soil, relying on natural processes for a healthier environment.
Diverse Crop Rotations And Polycultures
Growing a variety of crops in the same field, either at the same time or in different seasons, which can increase the resilience and productivity of the soil and the crops.
Legumes fix nitrogen, aiding plant growth; deep-rooted crops break hard soil, bringing up essential subsoil nutrients for healthier plants.
Polycultures can also reduce pest and disease pressure, as well as weed competition, by creating a more complex and balanced ecosystem.
Integrated Livestock Management
Raising animals in a way that mimics their natural behavior and integrates them with the crop production system.
Regenerative farmers practice rotational grazing—moving animals to fresh pastures, preventing overgrazing, soil compaction, and promoting grass regeneration.
The animals can also provide manure and urine, which can fertilize the soil and increase its organic matter content.
Agroforestry And Silvopasture
Combining trees and shrubs with crops and/or livestock, which can create a more diverse and productive landscape.
For example, regenerative farmers can plant fruit or nut trees among their crops, which can provide shade, windbreaks, and additional income.
They can also plant trees and shrubs in their pastures, which can provide fodder, shelter, and habitat for wildlife. Agroforestry and silvopasture can also help sequester carbon, conserve water, and prevent soil erosion.

Benefits Of Regenerative Farming?
This type of farming can offer multiple benefits for the environment, the farmers, and the consumers. Some of the main benefits are:
Climate Change Mitigation And Adaptation
Farming can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions by avoiding tillage, synthetic fertilizers, and pesticides, which can emit carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methane.
Boosts carbon sequestration, storing over 1 ton per hectare annually offsetting a car’s yearly emissions, says Rodale Institute study.
And also help farmers adapt to climate change by increasing the resilience and diversity of their crops and livestock, which can cope better with extreme weather events, pests, and diseases.
Food Security And Nutrition
This can help to improve food security by increasing the yield and quality of the crops and livestock, which can provide more food and income for the farmers and their communities.
Enhances nutrition with diverse, nutrient-rich food, delivering more vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and phytochemicals for consumers’ health benefits.
According to a study by the Food and Agriculture Organization, regenerative farming can increase crop yields by an average of 79%, and improve the nutritional value of the food by 69%.
Biodiversity And Ecosystem Services
Enhances biodiversity, creating diverse habitats for plants, animals, and microorganisms, restoring ecological balance and function in systems.
Help provide ecosystem services such as pollination, pest control, water purification, and soil formation, which can support the health and well-being of humans and nature.
How To Start Regenerative Farming?
It is not a quick fix or a magic bullet, but rather a long-term and holistic process that requires patience, experimentation, and adaptation.
This is also not a one-way street, but rather a two-way dialogue between the farmer and the land, which can learn from each other and co-evolve.
It’s a collective effort involving farmers, communities, and consumers sharing knowledge, resources, and values for sustainable agriculture.
If you are interested in starting regenerative farming, here are some steps that you can take:
Learn From The Experts
Many resources and examples of regenerative farming online, such as books, videos, podcasts, blogs, and websites.
Join regenerative farming networks like Regeneration International, Savory Institute, Soil Association, and Organic Consumers Association for support and promotion.
You can also visit and volunteer at regenerative farms near you, and learn from the farmers and their practices.
Assess Your Situation
Start by observing and analyzing your current farming system, such as the soil, the crops, the livestock, the water, the energy, the inputs, the outputs, the markets, and the challenges.
“Define farm goals, vision (production, methods, audience). Assess resources: land, labor, capital, skills, knowledge for success.”
Plan Your Transition
Design and implement a transition plan that suits your situation, your goals, and your resources and you can start small and simple, and gradually scale up and diversify.
You can also experiment and monitor, and adjust and improve your plan based on the feedback and results. You can also seek and accept help and advice from others, such as mentors, peers, experts, and consumers.
This is not only a way of growing food, but also a way of living and thinking, also a way of reconnecting with nature, with ourselves, and with each other.
It is a way of healing the planet, and feeding the world. It is a way of creating a more sustainable, resilient, and regenerative future for all.
Related Posts:
What Is The Definition Of Agriculture: Types, Benefits, Challenges & Future
Agricultural Hearths: Major Agriculture Hearths & Development
What Is Subsistence Agriculture Definition? Features, Issues
How To Grow Pomegranate From Cuttings: Major Steps, Tips & Tricks

Meet Our Expert Agricultural Administrator
Welcome to agrigreenhands.com, your dedicated hub for all things related to agricultural farming. Leading the way in our commitment to sustainable and innovative practices is Jawad Hussain, our esteemed administrator with a profound background in agriculture….


