Mechanization Of Agriculture, has transformed the way we cultivate crops and raise livestock. It’s a phenomenon that has reshaped the landscape of farming, bringing efficiency, speed, and precision to agricultural practices.
What Is Mechanization Of Agriculture?
Mechanization of agriculture refers to the integration of machinery and technology into farming processes to enhance productivity and streamline operations.
This transition from manual labor to machine-driven techniques has revolutionized the agricultural sector, marking significant advancements in crop cultivation, harvesting, and livestock management.
From the humble plow to sophisticated harvesting combines, mechanization has evolved over centuries, driven by innovation and the quest for increased efficiency.
Today, modern farms are equipped with an array of specialized machinery designed to perform various tasks, from soil preparation to post-harvest activities.

Motorized Mechanization Adoption Trends
The adoption of motorized mechanization has seen remarkable growth in recent decades. Small family farms and large agribusinesses alike have embraced mechanized solutions to meet the demands of modern agriculture.
Tractors, combines, and other farm implements have become staples on the farm, replacing traditional methods and manual labor.
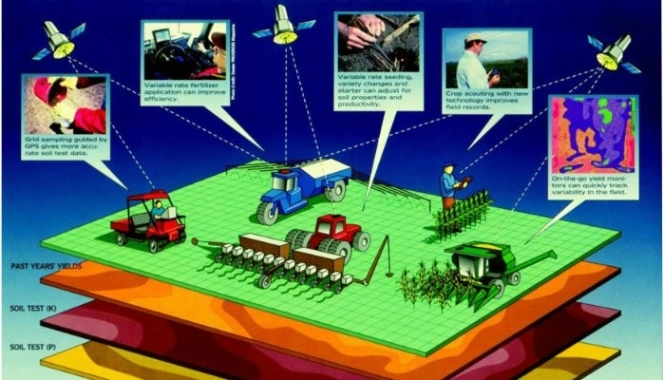
In developed countries, mechanization is widespread, with advanced technologies such as GPS-guided tractors and drones becoming commonplace. These technologies enable precise farming techniques, optimizing resource utilization and minimizing environmental impact.
In contrast, developing regions are experiencing a gradual shift towards mechanization, albeit at a slower pace due to various factors such as limited access to capital, infrastructure constraints, and cultural preferences for traditional farming methods.
However, initiatives aimed at promoting mechanization and providing support to small-scale farmers are gaining momentum, driving increased adoption in these regions.
Employment Impact
Mechanization of agriculture has sparked debates about its impact on employment in rural communities. While it’s true that mechanization has led to a reduction in the demand for manual labor, particularly in tasks such as plowing and harvesting, it has also created new opportunities in other areas.
Shifting Labor Dynamics
Mechanization of agriculture has led to significant shifts in labor dynamics within rural communities. Traditionally, agriculture has been a labor-intensive industry, relying heavily on manual labor for tasks such as planting, harvesting, and animal husbandry.
However, the advent of mechanized farming equipment has gradually reduced the demand for human labor in certain areas of agricultural production.
Decreased Demand For Manual Labor
One of the most noticeable impacts of mechanization on employment in agriculture is the decreased demand for manual labor. Tasks that were once performed manually, such as plowing fields or harvesting crops by hand, are now carried out more efficiently by machines.
As a result, fewer farm workers are needed to perform these tasks, leading to a decline in the number of agricultural laborers employed on farms.
Shift Towards Skilled Labor
While mechanization has reduced the demand for unskilled labor in agriculture, it has simultaneously created new opportunities for skilled workers.
Operating and maintaining complex agricultural machinery requires specialized knowledge and training, leading to an increased demand for skilled labor in the agricultural sector.
Tractor drivers, equipment technicians, and agricultural engineers are just a few examples of the skilled positions that have emerged as a result of mechanization.
Technological Advancements And Job Creation
Furthermore, the ongoing technological advancements in agriculture have opened up new avenues for employment in areas such as precision agriculture, data analysis, and agricultural robotics.
As farms become increasingly digitized and technology-driven, there is a growing need for workers with expertise in areas such as GIS mapping, drone technology, and software development.
These emerging fields offer exciting opportunities for employment and career growth in the agricultural sector, attracting a new generation of workers with diverse skill sets.
Preparing Land for Planting
One of the primary areas where mechanization has revolutionized agriculture is in land preparation. Traditional methods of plowing and tilling have been replaced by mechanized implements such as disc plows and cultivators.
These machines are not only faster but also more efficient, enabling farmers to prepare larger areas of land in less time.
Seed Drilling/Planting
The mechanized planting of seeds has significantly improved planting efficiency and crop uniformity. Seed drills, equipped with precision seeding technology, ensure accurate seed placement and spacing, leading to higher crop yields.
Moreover, mechanized planters are capable of planting large areas quickly, allowing farmers to take advantage of optimal planting windows.
Weeding/Crop Spraying
Weeding and pest control are critical aspects of crop management. Mechanized solutions such as herbicide applicators and crop sprayers have simplified these tasks, reducing the need for manual labor and chemical usage.
Additionally, advancements in precision agriculture have enabled targeted spraying, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing crop protection.
Harvesting
Perhaps the most significant impact of mechanization is seen in the harvesting process. Manual harvesting, once a labor-intensive and time-consuming task, has been revolutionized by harvesting combines and other specialized machinery.
These machines can efficiently harvest crops such as wheat, corn, and soybeans at a fraction of the time it would take using traditional methods.

Conclusion
Mechanization Of Agriculture, has ushered in a new era of efficiency and productivity in farming. From land preparation to harvesting, mechanized solutions have transformed every aspect of agricultural operations, enabling farmers to produce more with less effort.
While concerns about employment impact persist, mechanization continues to drive innovation and progress in the agricultural sector, ensuring food security and sustainability for future generations.
Read Also:
What Is O Farming: Make Money Online, Get Start & Benefits
Controlled Environment Agriculture: Cultivating The Future Of Farming
Terrace Farming: Unlock The Potential Of Sustainable Agriculture
O Farming Investing: Online Platform, Higher Returns & Low Risks
Farming Fixing And Fabricating: Save Money, For Your Better Life
O Farming In Dubai: A New Way To Grow Food In The Desert

Meet Our Expert Agricultural Administrator
Welcome to agrigreenhands.com, your dedicated hub for all things related to agricultural farming. Leading the way in our commitment to sustainable and innovative practices is Jawad Hussain, our esteemed administrator with a profound background in agriculture….


